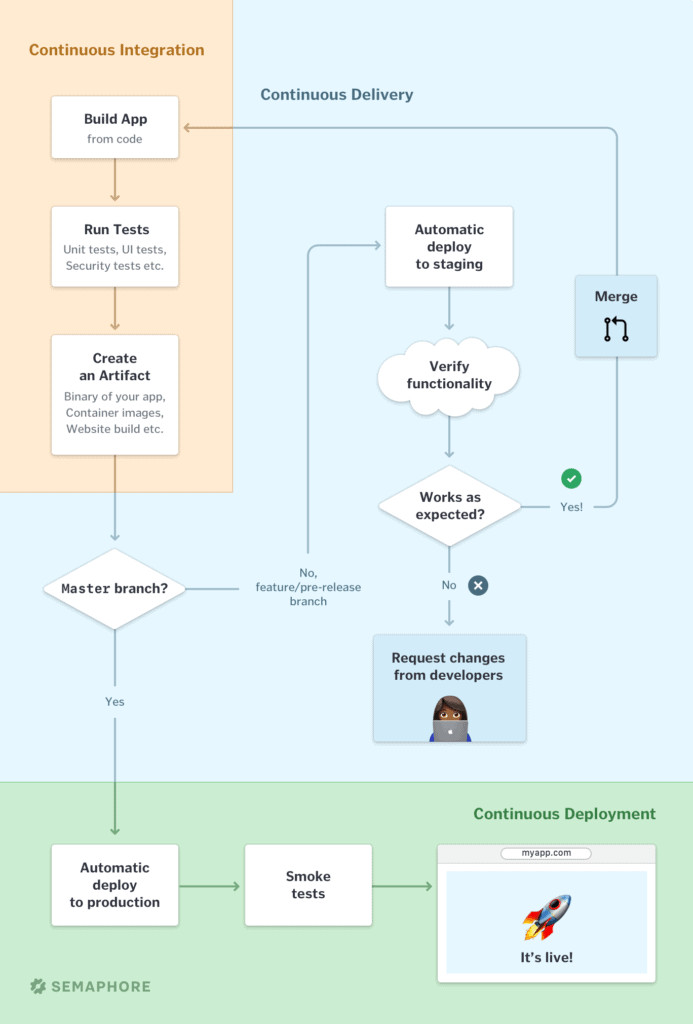
Continuous Integration, Delivery and Deployment
CI/CD Systems are used to speed up development and delivery.
The terms explained
- Continuous Integration
- Continuous Delivery
-
Image for clarity
"If any developer in your team can stop what they’re doing right now and ship the current development version of code to production in 20 minutes or less without anyone stressing about what could happen — congratulations, you’re doing CI/CD!"
Basic steps in a CI/CD Pipeline
Basic steps: Build - Test - Deploy Staging - Deploy Production
If using Docker and Kubernetes: Build - Test - Dockerize - Deploy to Kubernetes - Tag latest docker
Tools for CI/CD
Requirements for CI/CD
- Parallel computing systems for parallel tests etc.
Implementation
- CI
- Build Stage
- Code changes need to be compiled
- These days there is a need to pack them in Docker containers
- Automated Tests verify specific units of code like UI behaviour, API reliability, performance, etc.
- Maintain test reports
- Testing Stage
- Build Stage
- CD
- Deployment Stage
- Deployment Methods
- Deployment Stage
Tips for building a CI-CD pipeline
- Follow DevOps practices
Architecture
- Architect in a way that supports iterative releases - Avoid tight coupling between components
- Implement metrics that help detect issues in realtime (?)
- Developers should be able to deploy to staging for QA/manual testing
- All deployments should only involve the click of a button
Testing
- Run fast and fundamental tests first
- Always use same environment for testing
Triggers
- Include PRs, but Peer Review each PR
- In CD - Auto Deploy PRs merged to master
Improvement Tips
- Document flaky tests and improve them
- Optimize Feedback loop
- Invest in a CI/CD that can run tests in parallel stages.
- Improve slow tests